原文链接:https://oracle-base.com/articles/12c/multitenant-overview-container-database-cdb-12cr1,里面介绍了很多cdb和pdb在不同版本的特性,很全面,是很好的学习资源!
Oracle 12c Release 1 (12.1) introduced the Multitenant option. This article provides a basic overview of the multitenant option, with links to more detailed articles on the functionality.
- Overview
- Oracle Managed Files (OMF) and Multitenant
- Creating Pluggable Databases (PDBs)
- Unpluging and Plugging in Pluggable Databases (PDBs)
- Relocate a Pluggable Database (PDB)
- Refreshable Pluggable Database (PDB)
- Refreshable Pluggable Database (PDB) Switchover
- Proxy Pluggable Database (PDB)
- Application Containers
- Pluggable Database (PDB) Snapshot Carousel
- Container Database (CDB) Fleet Management
- Views
-
Multitenant Articles
- Non-CDB Architecture Deprecated
Overview
The multitenant option represents one of the biggest architectural changes in the history of the Oracle database. The option introduced the concepts of the Container Database (CDB) and Pluggable Database (PDB).
- Container Database (CDB) : On the surface this seems very similar to a conventional Oracle database, as it contains most of the working parts you will be already familiar with (controlfiles, datafiles, undo, tempfiles, redo logs etc.). It also houses the data dictionary for those objects that are owned by the root container and those that are visible to all PDBs.
- Pluggable Database (PDB) : Since the CDB contains most of the working parts for the database, the PDB only needs to contain information specific to itself. It does not need to worry about controlfiles, redo logs and undo etc. Instead it is just made up of datafiles and tempfiles to handle it's own objects. This includes it's own data dictionary, containing information about only those objects that are specific to the PDB. From Oracle 12.2 onward a PDB can, and should, have a local undo tablespace.
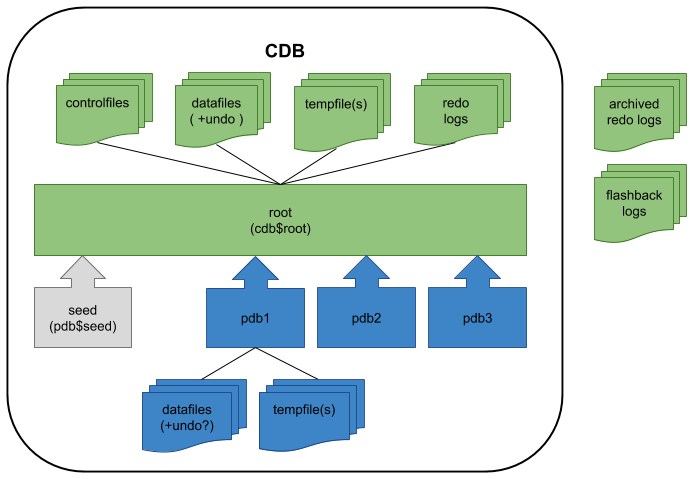
This split of the data dictionary between common objects, in the root container, and PDB-specific objects, in the PDB's data dictionary, is very important, because this separation is what gives the multitenant option its flexibility. From the perspective of the PDB, the data dictionary is the union of the root and PDB data dictionaries, so internally the PDB feels very much like a normal Oracle database. For example, theDBA_%andALL_%views within the PDB appears the same as any non-CDB database.
Oracle Managed Files (OMF) and Multitenant
Oracle recommend the use of Oracle Managed Files (OMF) when using the multitenant architecture, as it simplifies a number of pieces of functionality. It seems the use of OMF is mandatory for some functionality, like the Application Containers functionality in Oracle 12.2.
Creating Pluggable Databases (PDBs)
Since the bulk of the working parts are already present in the root container, creating a new PDB is a comparatively quick and simple task. When creating a completely new PDP, the PDB is created as a copy of a seed PDB, so it only takes as long as the files take to copy.
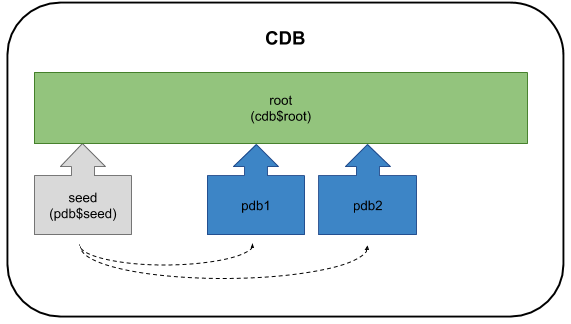
Instead of creating a new PDB from the seed, you can clone an existing PDB.
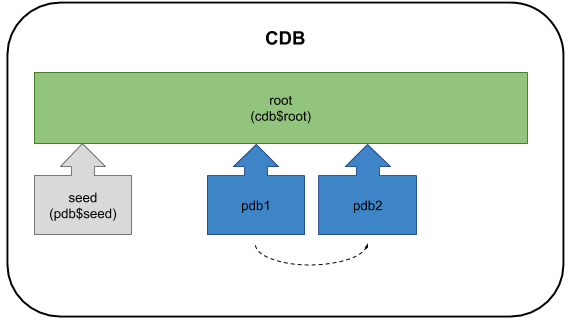
It is also possible to create clones in a remote CDB.
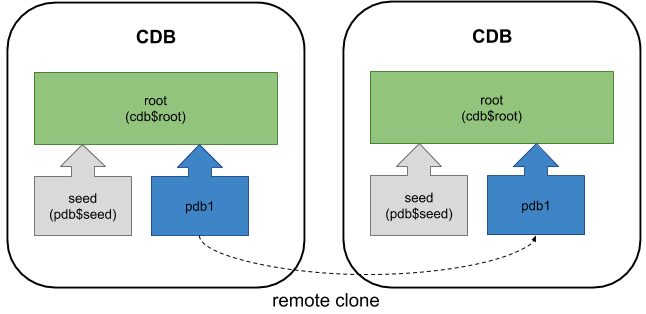
A more detailed description of creating and cloning PDBs can be found here.
Unpluging and Plugging in Pluggable Databases (PDBs)
One of the most powerful features of the multitenant option is the ability to unplug a PDB from a CDB and plug it back into another CDB.
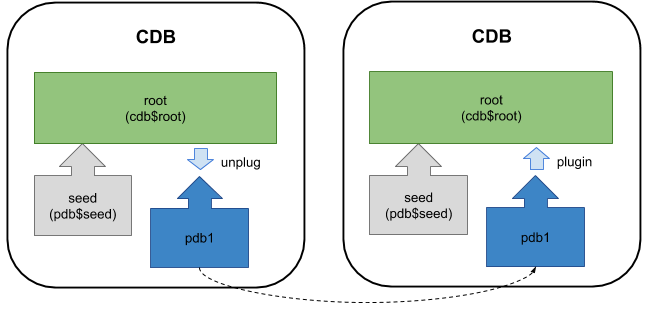
Not only does this allow databases to be moved easily, but it also provides an alternative way to patch and upgrade to future versions. An example of using unplug/plugin to perform a patch can be found here. A general discussion of the unplug/plugin mechanism is described here.
Conversion of a non-CDB database to a pluggable database involves getting a description the non-CDB database and using this to plug it into a CDB as a new PDB. This method is described here.
Relocate a Pluggable Database (PDB)
From Oracle 12.2 onward it is possible to relocate a PDB, moving it from one CDB to another. This is significantly simpler than doing a conventional umplug/plugin.
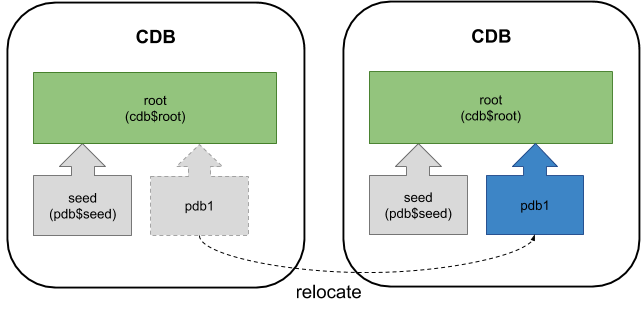
You can read about the relocating PDBs here.
Refreshable Pluggable Database (PDB)
From Oracle 12.2 onward it is possible to refresh a cloned PDB from the source PDB, provided it has only ever been opened in read-only mode.
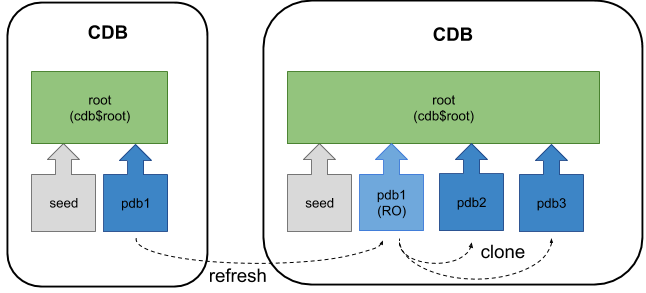
You can read about refreshing PDBs here.
Refreshable Pluggable Database (PDB) Switchover
From Oracle 18c onward it is possible to switchover a refreshable PDB.
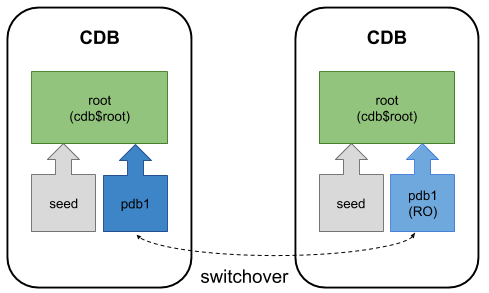
You can read about refreshable PDB switchover here.
Proxy Pluggable Database (PDB)
From Oracle 12.2 onward it is possible to create proxy PDB, which is a skeleton PDB that sends SQL across to a remote PDB to be processed. This allows you to have a local endpoint for a remote database.
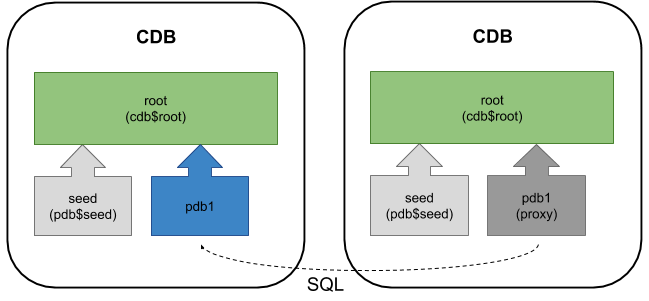
You can read about proxy PDBs here.
Application Containers
Oracle 12.2 introduces the concept of application containers, which act like a mini-root container. They can be used to centralise shared configuration and applications, which are used by their dependent application PDBs.
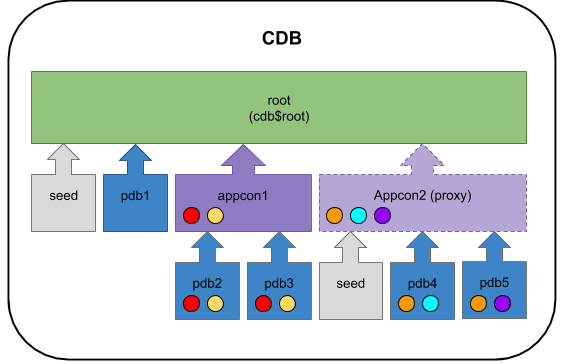
You can read about application containers here.
Pluggable Database (PDB) Snapshot Carousel
From Oracle 18c onward it is possible to create automatically managed snapshots of a PDB, also know as a snapshot carousel.
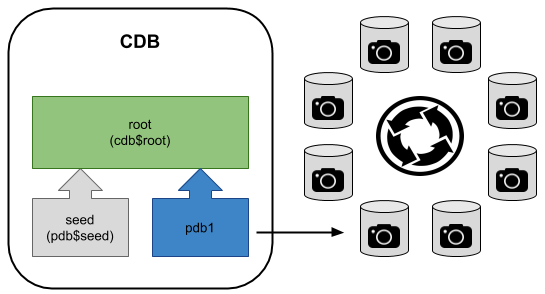
You can read about PDB Snapshot Carousel here.
Container Database (CDB) Fleet Management
From Oracle 18c onward it is possible to monitor multiple container databases centrally as a fleet.
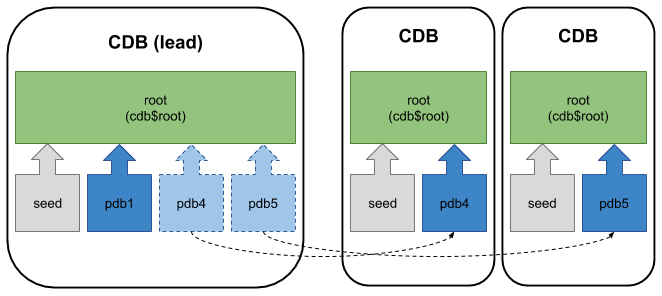
You can read about CDB Fleet Management here.
Views
The introduction of the multitenant option brings with it an extra layer of data dictionary views, allowing reporting across the root container and the pluggable databases (PDBs). Ignoring editions for the moment, prior releases had the following hierarchy.
DBA_ : All objects in the database. | --ALL_ : Objects accessible by the current user, including those |owned by the current user. --USER_ : Objects owned by the current user.
With Oracle 12c, an extra layer is added to the hierarchy.
CDB_ : All objects in all containers * (root and all PDBs).
|
--DBA_ : All objects in the current container (root or PDB).
|
--ALL_ : Objects accessible by the current user in the current container(root or PDB),
| including those owned by the current user.
--USER_ : Objects owned by the current user in the current container(root or PDB).
The views are described in the Reference Manual.
* The output of theCDB_views is dependent on the container they are accessed from. When accessed from the root container, they do indeed present all the information from all the containers. When accessed from a PDB, they effectively act like theDBA_views from within the container. This can be a little confusing at first.
Multitenant Articles
The following articles provide more detailed explanations of some of the concepts described in this article.
12.1.0.1 Onward
In 12.1 you can use a single PDB per CDB, also known as Lone-PDB, for free. If you want more than one PDB (2-252) you have to buy the Multitenant Option on top of Enterprise Edition.
- Multitenant : Pluggable Databases - What they will break and why you should use them anyway!
- Multitenant : Create and Configure a Container Database (CDB)
- Multitenant : Create and Configure a Pluggable Database (PDB)
- Multitenant : Prevent Accidental Creation of a Pluggable Database (PDB) - Lone-PDB
- Multitenant : Migrate a Non-Container Database (CDB) to a Pluggable Database (PDB)
- Multitenant : Connecting to Container Databases (CDB) and Pluggable Databases (PDB)
- Multitenant : Startup and Shutdown Container Databases (CDB) and Pluggable Databases (PDB)
- Multitenant : Configure Instance Parameters and Modify Container Databases (CDB) and Pluggable Databases (PDB)
- Multitenant : Manage Tablespaces in a Container Database (CDB) and Pluggable Database (PDB)
- Multitenant : Manage Users and Privileges For Container Databases (CDB) and Pluggable Databases (PDB)
- Multitenant : Backup and Recovery of a Container Database (CDB) and a Pluggable Database (PDB)
- Multitenant : Flashback of a Container Database (CDB)
- Multitenant : Resource Manager with Container Databases (CDB) and Pluggable Databases (PDB)
- Multitenant : Running Scripts in Container Databases (CDBs) and Pluggable Databases (PDBs)
- Multitenant : Database Triggers on Pluggable Databases (PDBs)
- Multitenant : Remove APEX Installations from the CDB
- Multitenant : Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) in Pluggable Databases (PDBs)
- Multitenant : PDBs With Different Time Zones to the CDB
- Multitenant : Pluggable Database (PDB) Names
- Multitenant : Upgrade a PDB using Unplug/Plugin
- Recovery Manager (RMAN) Database Duplication Enhancements : Multitenant Considerations
- Upgrade the Database Time Zone File Using the DBMS_DST Package - Multitenant
12.1.0.2 Onward
- Multitenant : Clone a Remote PDB or Non-CDB (12.1.0.2)
- Multitenant : Controlling PDB Replication in Data Guard Environments : STANDBYS Clause (12.1.0.2)
- Multitenant : Metadata Only PDB Clones (12.1.0.2)
- Multitenant : PDB Subset Cloning (12.1.0.2)
- Multitenant : PDB CONTAINERS Clause (12.1.0.2 and 12.2)
- Multitenant : PDB Logging Clause (12.1.0.2)
- Multitenant : USER_TABLESPACES Clause (12.1.0.2)
12.2.0.1 Onward
From 12.2 onward we are allowed to have a Proxy PDB, Application Root Container and a single user-defined PDB (regular or Application PDB) inside a single CDB without having to pay for the Multitenant Option. Notice we are still limited to a single user-defined PDB. The Multitenant Option still entitles you to 2-252 PDBs on regular kit, or 2-4096 PDBs on Oracle engineered systems or Oracle Database Clouds Services.
- Multitenant : Application Containers (12.2)
- Multitenant : Controlling PDB Replication in Data Guard Environments : ENABLED_PDBS_ON_STANDBY Parameter (12.2)
- Multitenant : Default Tablespace Clause During PDB Creation (12.2)
- Multitenant : Disk I/O (IOPS, MBPS) Resource Management for PDBs (12.2)
- Multitenant : Flashback Pluggable Database (PDB) (12.2)
- Multitenant : Hot Clone a Remote PDB or Non-CDB (12.2)
- Multitenant : Local Undo Mode (12.2)
- Multitenant : Memory Resource Management for PDBs (12.2)
- Multitenant : Parallel PDB Creation Clause (12.2)
- Multitenant : PDB Archive Files for Unplug and Plugin (12.2)
- Multitenant : PDB CONTAINERS Clause (12.1.0.2 and 12.2)
- Multitenant : PDB Lockdown Profiles (12.2)
- Multitenant : PDB OS Credentials (12.2)
- Multitenant : PDBs With Different Character Sets to the CDB (12.2)
- Multitenant : PDB Refresh (12.2)
- Multitenant : PDB Upgrades Using Priority Lists, Inclusion Lists and Exclusion Lists (12.2)
- Multitenant : Prevent Accidental Creation of a Pluggable Database (PDB) - Lone-PDB (12.2 Update MAX_PDBS)
- Multitenant : Proxy PDB (12.2)
- Multitenant : Relocate a PDB (12.2)
- Multitenant : Rename Services During PDB Creation (12.2)
- Multitenant : Resource Manager PDB Performance Profiles (12.2)
- Multitenant : Specify a Service When Switching Between Containers (12.2)
- Multitenant : Extended USER_TABLESPACES Clause (12.2)
- Resource Manager : Per-Process PGA Limits (12.2) (PDB and non-CDB)
- Heat Map, Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) and Automatic Data Optimization (ADO)
- Service-Level Access Control Lists (ACLs) - Database Service Firewall
18c Onward
Oracle 18c XE allows up to three user-defined PDBs for free. All other editions have the same rules as 12.2 regarding the Multitant Option.
- Multitenant Administrators Guide introduced for the first time.
- Multitenant : CDB Fleet Management
- Multitenant : Copying a PDB in a Data Guard Environment
- Multitenant : DBCA PDB Clone and DBCA CDB Duplicate
- Multitenant : Duplicate a Pluggable Database (PDB) to an existing Container Database (CDB)
- Multitenant : PDB Lockdown Profile Enhancements
- Multitenant : PDB Snapshot Carousel
- Multitenant : Refreshable PDB Switchover
- Multitenant : Upgrading to Oracle Database 18c
- Upgrading to Oracle Database 18c (Non-CDB) - Upgrade from 11.2 to 18c, including conversion to PDB.
- Multitenant : Usable Backups of Non-CDBs and Relocated PDBs (docs).
- Multitenant : Logical Partitioning - Container Maps (docs).
- Multitenant : Relocation of Sessions During Planned Maintenance (docs).
- Multitenant : Parallel Statement Queuing at the PDB Level (docs).
- Multitenant : Split Mirror Clone PDBs (docs).
- Multitenant : Create a Keystore for Each Pluggable Database (docs).
Multitenant Option: CDBs and PDBs - YouTube Playlist
19c Onward
- Enhancements to database-managed PDB snapshots (docs).
- Workload capture and replay in a PDB (docs, docs).
- ADDM analysis for PDBs (docs, docs).
- Support for multiple PDB shards in the same CDB (docs).
- Fine-grained single-instance PDB patching (docs).
- Cloning a remote PDB using DBCA (docs).
- Remote PDB relocation (docs).
- Cloud object store support for Data Pump Import (docs, docs).
- Database Vault Operations Control for infrastructure database administrators (docs).
Non-CDB Architecture Deprecated
With the release of Oracle Database (12.1.0.2), the non-CDB architecture has been deprecated. Some 12c features do not currently work with the multitenant architecture (see here), so depending on the features you require, you may still need the old pre-12c style instances.
Remember, using a single PDB does not require the Multitenant option, so lone-PDB setups can be used at no extra cost, allowing you to get familiar with the multitenant architecture.
From 12.2 onward we are allowed to have a Proxy PDB, Application Root Container and a single user-defined PDB (regular or Application PDB) inside a single CDB without having to pay for the Multitenant Option. Notice we are still limited to a single user-defined PDB.
For more information see:
- Introduction to the Multitenant Architecture
- Overview of the Multitenant Architecture
- Managing a Multitenant Environment
Hope this helps. Regards Tim...

